
Lab Safety
Recognize, Assess, Minimize, Prepare for Hazards

There are a variety of hazards that may be found in a laboratory. Know the hazards of the materials you will work with. Read lab safety and experiment procedures, chemical SDS and agent biosafety summaries/practices before starting. Safety is everyone's responsibility. Don't allow yourself to become complacent over time. Consider others and maintain a clean working environment. Please email us at EHS@uhcl.edu if you need assistance with resources or information on requirements.
Lab Safety Training
See the Laboratory Training Matrix for what is required to conduct work in a UHCL lab.
Training Enrollment
Students taking laboratory courses utilizing chemicals are enrolled at the beginning of every semester in Lab Safety Training within Canvas. Late registering students must email coen@uhcl.edu for enrollment.
Advanced Lab Safety Training course is required for TA's, RA's, Graduate Independent Studies, and Lab Faculty and Staff.
Additional lab specific trainings are available as modules within the Canvas Lab Safety Training Topics course.
Training Courses
These training presentations may be taken in Canvas. See the Lab Training Matrix for a list of what training and frequency is required for your lab.
- Lab and Chemical Safety Training - including Hazard Communication, fire and emergencies, first aid, bloodborne pathogens awareness
- Safety in Academic Chemistry Laboratories - American Chemical Society Publication (resource)
- Chemical Labels and Labeling - Relabeling original containers, labeling Secondary containers (prepared solutions, samples), Waste labels
- Fume Hoods User Training
- Waste handling, Collection & Labeling
- Autoclave, Disinfection, and Blood Borne Pathogens Training
Videos
- Lab Safety Institute Favorites
- Chemical Safety Board Videos- search for Experimenting with Danger, and After the Rainbow
Humorous Videos
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
PPE may be purchased at the bookstore. If purchased elsewhere, it must match the same protection as those chosen for sale at the bookstore. i.e., same length lab coat down legs and long sleeves, same size and design safety glasses and goggles with indirect vents and Z87 impact rating.
Lab Coats
Lab coats must be full length to the knees with long sleeves. Dental coats or doctors coats do not provide sufficient coverage. A blend of polyester and cotton is recommended to retain both liquid and flame retardant properties. 100% polyester lab coats shall not be used with flammable or pyrophoric materials. 100% cotton absorbs chemicals more easily and burns hotter in a fire if they do catch fire.
Safety Goggles
Safety goggles with indirect vents are required for use with liquids, as the risk of splash and drip into the eye is present. Safety goggles should fit the face well to provide a seal. Safety glasses may be used with dry materials, and are chosen to provide the most face coverage.
Gloves
Gloves are not suitable for use with every chemical. There are many types of glove materials. Each type is compatible and incompatible with different materials. Search by chemical for the recommended glove type, and then by the manufacturer for breakthrough time (length of time use) for that glove thickness.
- Example: Best Brand N-Dex regular disposable gloves are not suitable for concentrated sulfuric acid. They have a breakthrough time of 10 minutes or less.
- Some Different Glove Types and Uses
- Glove Selection by Chemical Search-Cole Parmer
- Chemical Resistance Guide - Permeation & Degradation Data
Chemical Inventory
The UHCL Chemical Inventory is compiled within the OnSite Environmental Health & Safety Assistant (EHSA) software. Chemical inventory is required by law annually, and serves several functions:
- To know what materials are present and assess their hazards
- A list of SDS needed, and repository to store SDS for reviewing hazards of chemicals used, hazard planning, training and first aid purposes
- Use for several agency reports (e.g., DEA, TCEQ, DSHS)
- Allow faculty to share or dispose of items.
- Chemical Inventory Template for Import into OnSite
- Requirement and Completion information
- Notice to Employees, and en español
Purchase Approval for Chemicals
Purchase requests for Chemicals are reviewed by EHS.
Chemicals listed in the CHP High Hazard / Toxic Chemicals Appendix 5 require approval. Purchase requests must include those chemical's:
- SDS
- SOP created per CHP template, with faculty name and location, SOP user training signoff
- Requesting Faculty's CHP Review Acknowledgement
Hazards of chemicals requiring this include, but are not limited to the following (review the CHP list and SDS to determine):
- Carcinogens
- Highly Toxics
- Acutely Toxics
- Pyrophorics (air and/or water reactive)
- Explosives and Peroxide-Forming, Potentially Explosive Chemicals (PEC's)
- Antineoplastics
- Nanoparticles
Approval for use of these chemicals will be reviewed by EHS and/or the Research Safety Committee per the CHP.
All Hazardous Chemicals must have Safe Operating and handling Procedures (SOP), SDS, appropriate handling equipment, PPE, and training in place for all users / workers.
All Chemicals must be included in each lab Inventory, with Safety Data Sheet (SDS) on hand. SDS's may be satisfied after uploading chemical inventory to EHSA software and all lab workers are submitted and made users in the software (SDS linked in software inventory screen). SDS may also be printed and kept in Lab Safety binder. Workers must be informed of the chosen SDS location.
Biological Safety
- UH-Biological Safety Manual
- UHCL Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan
- UHCL Autoclave, Disinfection, and Blood Borne Pathogens Training for Labs (taken in Canvas, Lab Safety Training Topics)
- Autoclave Procedures
- Autoclave Log and Efficacy Testing Sheets
- Autoclave Bag Tags
See below for Biological Safety Cabinet and Fume Hood use information.
Incident Reporting
All incidents and injuries on campus or University business must be reported online within 24 hours.
If you witness an incident, a witness statement must be submitted.
Go to the Incident Reporting Forms section on the EHS Forms page for online forms for employees, students and visitors, and witnesses. Paper / pdf forms are no longer accepted.
Safety Concern, Near Miss & Equipment Incident Report Form
In the same way accidents/incidents are investigated for actions to prevent recurrence, it is important to learn from near misses and eliminate unsafe conditions to prevent an accident from actually occurring.
UHCL asks that all employees report and correct potential hazards concerns and near misses immediately to help prevent incidents and maintain a safe work environment. Incidents that result in damage to equipment must also be reported within 24 hours. Submit these reports to EHS@uhcl.edu.
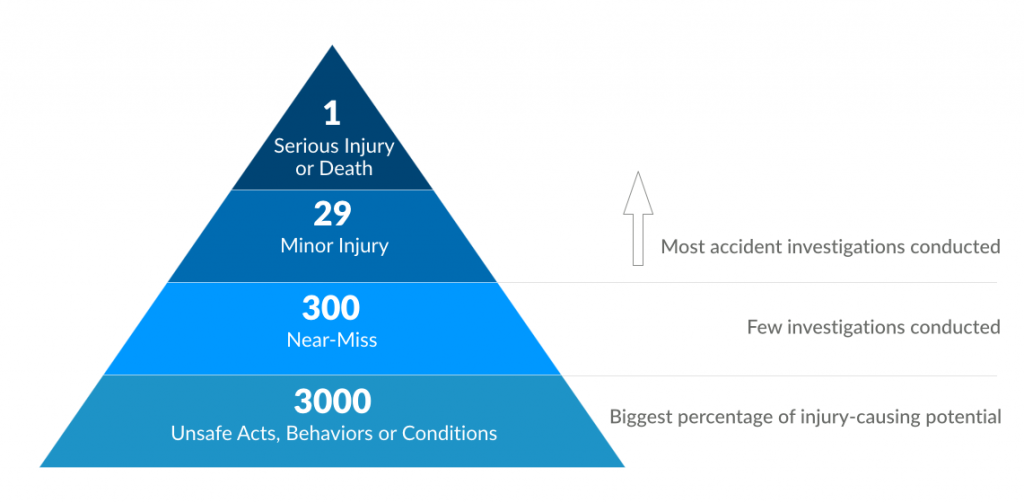 (Accident theory model illustration by Heinrich & Bird)
(Accident theory model illustration by Heinrich & Bird)
Environmental Health and Safety Assistant (EHSA) Software
UHCL uses this software to keep track of regulatory obligations, chemical inventories, SDS, inspections, etc. Login is the same as your UHCL user id and password. User logins must be setup first by EHS for software access.
There is also a searchable database hub for SDS in EHSA. This separate link does not require user login setup, and can be used by all UHCL credentials.
Fume Hoods, Biosafety Cabinets
Labs may be equipped with chemical fume hood(s) and/or biological safety cabinets. Here is information on safe work practices, how they work, and a decision matrix for selecting the right one.
Chemical Fume Hoods
- Fume Hoods User Guide training
- User Information Posted on fume hoods
- Fume Hood diagram and Safety Reminders
- Fume Hood Containment illustrations
Biological Safety Cabinets
Laser Safety
All class 3b and 4 lasers must be approved and registered with the state. New laser proposals, locations, and authorized users must be requested by sub-registration application or amendment to the Laser Safety Officer (LSO) x.2107 to obtain prior authorization and training (4 hour in person) scheduled with LSO and Laser faculty.
- Notice to Employees: Texas Regulations for Control of Radiation
- Laser Safety Awareness & Refresher Training - for guests and visitors (taken in Canvas, Lab Safety Training Topics)
- Laser Safety Awareness Simple Training - for visitors
- UHCL Certificate of Registration for Lasers - License with the State
- Laser Safety Manual UHCL
- Laser Sub-registration form - for new Laser PI's
- Laser Sub-registration Amendment form - to request new lasers or users
Laser Regulations and Requirements
Radiation Safety
All radioactive source materials, locations, authorized users, and equipment containing sources must be approved and registered with the state on our license.
Any changes in radiation source, use, equipment, locations, or users must be requested by Amendment application Form (below) to the Radiation Safety Officer (RSO) x.2107 for requirements review (training, procedures, setup) and subsequent RSO submission to the state (for most changes) to receive permission for an amendment to the present radiation license, prior to activities. Expect at least a month turnaround time.
New activities, users, and equipment, PI's may petition via application below. Expect longer turnaround time for review, controls, and application amendment with the RSO and state.
- Notice to Employees: Texas Regulations for Control of Radiation
- Application for PI/Isotope/Equipment (new PI sub-license)
- Amendment Form (to update users, isotope, equipment use)
- RSO Duties and Responsibilities
- UH Radiation Safety Enforcement reference
Radioisotope Regulations
- Texas Health and Human Services: Laws and Rules - Radioactive Materials Licensing
- 25 TAC 289.252 Licensing of Radioactive Material
- 25 TAC 289.228 Radiation Safety Requirements for Analytical Machines
- 25 TAC 289.231 General Provisions and Standards for Protection Against Machine Produced Radiation
- 25 TAC 289.255 Radiation Safety Requirements for sources of radiation used in machines
X-Ray Safety Program
All equipment producing x-rays must be approved and registered with the state. New equipment proposals and new authorized users must be requested by sub-registration application or amendment to the X-ray Radiation Safety Officer (XRSO) x.2107 to obtain prior authorization and training.
- X-Ray Radiation Safety Manual
- X-Ray Equipment Application (sub-registration to request new equipment)
- X-Ray Equipment Amendment Form (to update users or equipment use)
- UHCL Certificate of Registration for X-Ray Registration - License with the State
- Notice to Employees: Texas Regulations for Control of Radiation
X-Ray Regulations
- Texas Health and Human Services: Laws and Rules - X-Ray Machines and Services
- 25 TAC 289.226 Registration of Radiation Machine Use and Services
- 25 TAC 289.227 Use of Radiation Machines in the Healing Arts
- 25 TAC 289.228 Radiation Safety Requirements for Analytical Machines
- 25 TAC 289.231 General Provisions and Standards for Protection Against Machine Produced Radiation






